Radon Testing
What is radon? – Radon is a naturally occurring underground radioactive gas. It is element number 86 on the periodic table with a symbol of Rn. It occurs naturally as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chain where uranium slowly decays into lead. Uranium is naturally present in rocks, such as granite and shale and can be found everywhere in the world. Unfortunately, Ohio’s soils contain a large amount of this radon producing uranium. Because radon is a gas, it moves easily through the soil to the surface. You cannot see, taste, smell or feel radon. Radon is found everywhere in varying amounts. Radon levels are measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L). A picocurie is a measure of radioactivity. When radon reaches the surface outside, it immediately dilutes into the surrounding air. Radon levels outside average 0.4 pCi/L.
How does radon hurt us? - Radiation from radon and it’s immediate decay products is weak radiation. This radiation cannot pass through our skin, so cannot harm us if it hits our skin. The problem is, it is airborne. When we breath it in, this radiation -can- penetrate and damage our lung tissue. The burst of energy from this radiation can damage the DNA in our lung tissue. In some cases, if the lung tissue does not repair the DNA correctly, the damage can lead to lung cancer. According to the U.S Surgeon General, radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers.
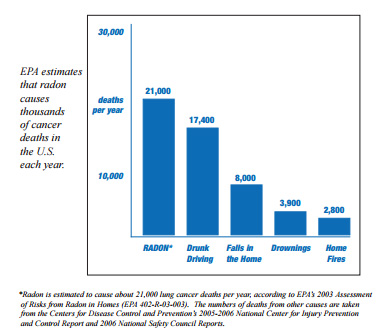
Is it really a health risk in my home? – Radon has always been present in our environment. Humans have always been exposed to the average 0.4 pCi/L levels outside, so we have always had some health risks from radon. The problem is, radon levels can accumulate in homes to much higher levels. Slight negative pressure in our homes caused by furnace and water heater exhaust vents, bathroom vents, dryer vents, and something called the 'stack effect' pulls radon laden air from the soil beneath our homes. It enters through minute cracks and openings in the foundation. We build our homes tighter and tighter to save energy, but this traps this air in our homes. This air is dispersed throughout our homes by our HVAC systems. All homes can have high radon levels, even homes built on slabs or crawlspaces. While there is no safe level of radon, the EPA has set an ‘action level’ of 4.0 pCi/L. If the average radon level in your home is 4.0 pCi/L or higher, the EPA recommends you take steps to lower the radon level. It is not unusual to find radon levels in Central Ohio homes of 4.0 to 10.0 pCi/L. Seventy-five percent of the homes we test measure 4.0 pCi/L or higher.
Is it possible to lower the radon level in my home? – Yes. Radon mitigation systems are effective, not too hard to install, and not too costly. The most effective way to lower radon in most homes is to install a sub-slab depressurization system. A hole is cut in your basement floor and radon laden air is sucked out and piped outside your home. Crawlspace floors are sealed with plastic and air underneath also pumped out. Wall / floor seams will be caulked and sump pump lids sealed. The typical cost for an average home in the Columbus area is $1200 - $1700.
Still not convinced? - Here are some additional resources:
Ohio Department of Health Radon in Ohio Homes
US EPA Radon – www.epa.gov/radon
US EPA Home Buyer's and Seller's Guide To Radon
CDC Radon - www.cdc.gov/features/protect-home-radon/index.html
OnSite Property Inspections is licensed by the State of Ohio to perform radon tests. We use state of the art continuous radon monitoring equipment. Results are immediately available at the conclusion of the required 48 hour test. We typically do a radon test as an add-on to a Buyer's home inspection.
Please call or email us if you have questions.